Android Nomad #53 - Android Domain Interview
FAQs

1. What is the Android operating system?
The Android operating system is a Linux-based mobile platform developed by Google, designed primarily for touchscreen devices such as smartphones and tablets. It provides a user-friendly interface, extensive app ecosystem via Google Play Store, and adaptability for diverse hardware configurations. Its architecture includes the Linux kernel, libraries, runtime, application framework, and system apps, making it powerful for both users and developers.
2. Describe the four main Android app components.
The four main Android app components are:
- Activities: Represent a single screen of the app’s UI, like a login page. Activities handle user interaction.
- Services: Run background operations, such as playing music or syncing data, without a user interface.
- Broadcast Receivers: React to system-wide events, like receiving an SMS or detecting low battery.
- Content Providers: Manage data sharing between applications, such as accessing a contact list.
Each component has a specific role in building a complete, interactive application.
3. What are the Intents in Android?
Intents are messaging objects used to communicate between app components. They enable activities, services, and broadcast receivers to interact seamlessly.
- Explicit Intents specify the target component directly, such as starting a specific activity.
- Implicit Intents declare a general action, like sharing data, and allow the system to choose the best app for the task.
For example, an app can use an implicit intent to open a web page in the browser.
4. How can you explain the Android app life cycle?
The Android app lifecycle describes the sequence of states an app goes through during its existence, managed by callback methods:
- onCreate(): Initializes the activity.
- onStart(): Makes it visible to the user.
- onResume(): Brings it to the foreground.
- onPause(): Partially hides it.
- onStop(): Completely hides it.
- onDestroy(): Cleans up before termination.
Understanding these states ensures efficient resource management and smooth user experiences.
5. How do you handle screen orientation changes in Android?
When a device’s orientation changes, the current activity is destroyed and recreated. To preserve the app state:
- Use
onSaveInstanceState()to store transient data. - Restore the data using
onRestoreInstanceState()oronCreate()during the new activity instance's lifecycle.
Alternatively, handle configuration changes manually by specifying configChanges in the manifest.
6. What is an Android Manifest file?
The Android Manifest file is an XML file that declares essential app information to the system. It specifies components like activities, services, and broadcast receivers, along with required permissions, hardware features, and metadata. For example, it declares whether an app needs internet access or supports specific screen orientations.
7. What is the significance of the Context class in Android?
The Context class is a gateway to application resources and services. It facilitates access to:
- System services (e.g., location, notifications).
- Resource files (e.g., strings, layouts).
- Application data (e.g., shared preferences, database).
Activities, application instances, and services provide specific types of Context that developers use depending on their needs.
8. What are Layouts in Android?
Layouts define how UI elements are arranged in an Android application.
- LinearLayout: Aligns elements in a single direction (horizontal or vertical).
- ConstraintLayout: Offers a flexible way to position UI elements using constraints.
- RelativeLayout: Positions elements relative to each other or the parent.
Choosing the right layout ensures an optimized and responsive design across different screen sizes.
9. How would you explain the difference between a ScrollView and a RecyclerView?
- ScrollView: Best for displaying a static, vertically scrollable list of views.
- RecyclerView: Designed for dynamic or large datasets, providing efficient memory management by reusing item views through a ViewHolder pattern.
Use ScrollView for simpler needs and RecyclerView for performance-critical, interactive lists.
10. How would you create a custom view in Android?
Creating a custom view involves:
- Extending the
Viewclass or a subclass. - Overriding methods like
onDraw()for custom rendering andonMeasure()for size handling. - Adding XML attributes if customization is required.
- Using the view in your layout or adding it programmatically.
This approach is ideal when standard widgets don’t meet your design needs.
11. What is the difference between dp, sp, pt, and px?
- dp (density-independent pixels): Ensures consistent UI element size across screens.
- sp (scale-independent pixels): Similar to dp but scales with user font preferences; used for text.
- pt (points): Rarely used; 1/72 inch and doesn’t adapt to density.
- px (pixels): Exact screen pixels, which vary by density, making it less ideal for layouts.
For scalable designs, use dp for layouts and sp for text.
12. How would you explain the concept of Fragments?
Fragments are modular sections of an activity’s UI. They are used for creating dynamic and flexible user interfaces. Fragments enable reuse within multiple activities and support multi-pane layouts, especially on larger screens like tablets.
For example, a messaging app can use fragments for a contact list on the left and a chat view on the right.
13. What is Shared Preferences?
Shared Preferences is a lightweight mechanism to store key-value pairs of primitive data types. It’s ideal for saving user settings or small amounts of app state data. Access it via SharedPreferences API, and store data securely with MODE_PRIVATE when needed.
14. How to use SQLite in Android?
SQLite is a lightweight relational database embedded in Android, making it an excellent choice for local data storage.
Steps to use SQLite in Android:
- Create an SQLiteOpenHelper: This class simplifies database management by handling creation and versioning.
- Override
onCreate()andonUpgrade(): Define the schema and manage changes to it over time. - Access the Database: Use
getReadableDatabase()orgetWritableDatabase()for read/write operations. - Perform Data Operations: Use methods like
insert(),update(),delete(), or execute raw queries usingquery()andrawQuery(). - Close Connections: Always close the database after operations to free resources and avoid memory leaks.
For instance, SQLite is great for storing app-specific data like user preferences or offline caches.
15. How do you perform a background task in Android?
Android offers multiple approaches to run background tasks, ensuring a responsive UI:
Services:
Foreground Services: Used for noticeable tasks like music playback, requiring a persistent notification.
IntentService: Ideal for one-time tasks that stop automatically after completion.
ThreadPoolExecutor & Handlers: Enable concurrent execution of lightweight tasks while maintaining communication with the main thread.
WorkManager: A modern API for scheduling deferrable and guaranteed tasks that persist across app restarts. Suitable for tasks like periodic data syncing.
Always ensure background tasks don’t overload system resources or block the UI thread.
16. What is a Loader?
A Loader simplifies asynchronous data loading in Android applications. It is often used to fetch data from a database or a server while avoiding UI thread blockage.
Key benefits:
- Lifecycle Awareness: Automatically reconnects to existing data after configuration changes like rotations.
- Efficiency: Prevents reloading of data unnecessarily.
Although Loaders have been largely replaced by modern libraries and patterns like LiveData and ViewModel, they are still useful in legacy applications.
17. What is the Room Persistence Library, and why is it useful?
The Room Persistence Library is part of Android's Architecture Components, offering an abstraction over SQLite to simplify database operations.
Key Features:
Provides compile-time verification of SQL queries, reducing runtime errors.
Supports observable data with LiveData, Flow, or RxJava.
Ensures simpler and more maintainable code compared to raw SQLite.
Room integrates seamlessly with the Jetpack ecosystem, making it the go-to choice for database management in modern Android development.
18. How to make a network request on Android?
Making network requests in Android often involves libraries like Retrofit or OkHttp to simplify HTTP operations.
Steps to make a network request:
- Set Permissions: Add the
INTERNETpermission in the manifest file. - Initialize the Library: Define API endpoints and configure the library.
- Perform Operations: Make requests asynchronously to prevent UI thread blocking.
- Handle Responses: Process the results or errors appropriately.
For example, Retrofit allows easy integration with REST APIs and supports Kotlin coroutines for asynchronous calls.
19. What libraries can be used for networking in Android?
Several libraries enhance networking in Android by abstracting complex tasks:
- Retrofit: A type-safe HTTP client by Square, ideal for RESTful APIs. Its integration with Gson and Kotlin coroutines simplifies asynchronous operations.
- OkHttp: A foundational HTTP client for tasks like caching, connection pooling, and monitoring. Often used under the hood by other libraries.
- Volley: Designed for lightweight, bursty requests, providing rapid caching and streamlined response handling.
These libraries are tailored to specific needs, with Retrofit being the most popular for modern development.
20. How do you handle caching in Android?
Caching improves app performance by reducing network calls and reusing data efficiently.
- Shared Preferences: Store lightweight data like user settings.
- SQLite or Room: Manage structured data persistently.
- Glide/Picasso: Cache images for smoother loading.
- Retrofit with OkHttp: Cache HTTP responses for offline access.
- Custom Cache Implementation: Use the
Cacheclass for advanced or unique requirements.
Caching strategies depend on the type of data and app requirements.
21. How can you secure data transmission in Android?
To secure data transmission, follow best practices to protect sensitive information:
- Use HTTPS: Ensures encrypted communication between the app and server.
- Implement SSL/TLS Pinning: Mitigates man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Encrypt Sensitive Data: Use AES or other robust encryption algorithms.
- Token-Based Authentication: Restrict API access with secure tokens.
- Minimize Data Exposure: Transmit only what is necessary.
Always validate third-party libraries to avoid introducing vulnerabilities.
22. How do you find memory leaks in Android apps?
Memory leaks occur when objects are retained in memory but are no longer in use.
- Memory Profiler: Available in Android Studio, it tracks memory usage, analyzes heap dumps, and identifies retained objects causing leaks.
- LeakCanary: A third-party library that detects and notifies about leaks during runtime.
Proactively testing with these tools ensures better resource management and a smoother user experience.
23. How can you improve the performance of a ListView?
Enhance ListView performance with the following strategies:
- ViewHolder Pattern: Reduces repeated
findViewById()calls. - Recycling Views: Use
convertViewin the adapter’sgetView()method to reuse existing views. - Lazy Loading: Load images or data incrementally for smoother scrolling.
- Flat Layouts: Avoid deeply nested views to reduce rendering complexity.
- Pagination: Load data in chunks for long lists to improve memory usage.
Testing and profiling regularly ensures ListView remains performant.
24. How to debug ANRs and crashes in Android?
Debugging ANRs (Application Not Responding) and crashes requires a methodical approach:
ANRs:
Analyze the
traces.txtfile to identify blocking code.Optimize long-running tasks by moving them off the main thread.
Crashes:
Use Logcat in Android Studio to trace the stack and identify crash causes.
Leverage Android Profiler for insights into resource usage and bottlenecks.
Reproducing issues in a controlled environment and stepping through code using the debugger aids in resolving these problems effectively.
25. How do you optimize the performance of an Android application?
Optimizing Android app performance involves strategies such as:
- Using tools like Android Profiler to monitor CPU, memory, and network usage.
- Reducing APK size with ProGuard and removing unused resources.
- Implementing lazy loading for large datasets and images.
- Utilizing background threads like Coroutines for long-running tasks.
- Minimizing third-party libraries and testing across diverse devices for consistent performance.
26. What are the different ways to schedule tasks in Android?
- AlarmManager: For time-specific tasks, even if the app isn't active.
- JobScheduler: For tasks based on conditions (e.g., network connectivity).
- WorkManager: For guaranteed, deferrable tasks.
- Handler/Looper: For short, repetitive tasks on the main thread.
- Timer: For fixed-rate or fixed-delay execution.
- ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor: A Java-based alternative for generic scheduling.
27. How can you explain the concept of Services in Android?
Services perform background tasks without a user interface. Examples include:
- Bound services: Allow interaction with other app components.
- Unbound services: Operate independently, such as a music player continuing playback when the user navigates away.
28. What is Data Binding?
Data Binding links UI components directly to data sources in XML layouts, enabling automatic updates when data changes. It reduces boilerplate code and improves responsiveness by automating UI updates.
29. How does ProGuard work?
ProGuard:
- Shrinks code by removing unused classes and methods.
- Optimizes bytecode for performance.
- Obfuscates code by renaming classes, fields, and methods to enhance security. This process ensures smaller APKs and harder-to-reverse-engineer apps.
30. What is Dependency Injection? Provide examples with Dagger.
Dependency Injection provides objects their dependencies externally.
Dagger Example:
- Annotate dependencies (
@Inject) and modules (@Module) to let Dagger create and provide them.
E.g., ACarclass with an injectedEngineeliminates manual instantiation, improving modularity and testability.
31. How do you perform unit testing in Android?
- Use JUnit for unit tests.
- Employ Robolectric or Espresso for Android-specific testing.
- Mock dependencies with Mockito.
- Automate tests with CI tools like Jenkin
32. How would you explain the importance of the Espresso testing framework?
Espresso enables precise UI testing by simulating user interactions. It ensures:
- Functional correctness of the UI.
- Bug-free user experiences, particularly for complex applications.
- It is essential for maintaining quality in dynamic UI environments.
33. How can you describe the Android app deployment process?
The Android app deployment process includes:
- Testing and building a release APK.
- Signing the APK with a private key.
- Uploading to Google Play Store for review.
- Post-approval, the app is available for download, with regular updates for compatibility and security.
34. What are the different build types in an Android project?
- Debug: Used during development, with debugging enabled and no optimization.
- Release: Optimized and secure for distribution to users, with debugging disabled.
35. How can you Explain the difference between val and var in Kotlin?
val: Immutable; its value cannot change after initialization.var: Mutable; its value can be updated.
Usevalfor constants andvarfor variables requiring modifications.
36. How does Java Garbage Collection work in Android?
Java Garbage Collection in Android uses an automatic memory management process to reclaim memory occupied by objects no longer in use.
Key Points:
- Algorithm: It primarily uses the mark-and-sweep algorithm. Objects are marked as "reachable" or "unreachable", and those not reachable are swept away.
- Avoiding Leaks: Developers must nullify references to objects that are no longer needed, especially in contexts like activities or fragments, to avoid memory leaks.
- Performance: While it optimizes memory, garbage collection pauses can cause performance hitches if the app generates excessive garbage.
37. How Null Safety is achieved in Kotlin?
Kotlin ensures null safety by making all variables non-nullable by default, eliminating the risk of null pointer exceptions (NPEs).
Techniques for Null Safety:
- Nullable Types: Declare variables nullable using the
?modifier (e.g.,val name: String?). - Safe Calls (
?.): Use to access properties/methods on nullable objects safely. - Elvis Operator (
?:): Provides a fallback value if a variable is null. - Null Assertion (
!!): Forces access to nullable variables but throws an exception if null. Use cautiously.
38. What are the differences between == and === in Kotlin?
==(Structural Equality): Compares the values/contents of objects. Equivalent to.equals()in Java.===(Referential Equality): Checks if two references point to the same object in memory.
39. How do you handle exceptions in Java and Kotlin?
Exception handling ensures stability and proper error management in Android apps.
- Java:
Usetry-catch-finallyblocks. Example:
try {
// Risky code
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle exception
} finally {
// Cleanup code
}- Kotlin:
Kotlin simplifies exception handling with concise syntax and allows catching multiple exceptions usingwhen. Example:
try {
// Risky code
} catch (e: Exception) {
when (e) {
is IOException -> handleIOException()
is NullPointerException -> handleNPE()
}
} finally {
// Cleanup code
}40. What is the MVP architecture?
MVP (Model-View-Presenter) is an Android architectural pattern that separates application logic from UI components.
- Model: Manages data and business logic (e.g., fetching data).
- View: Displays data to the user and sends user inputs to the Presenter.
- Presenter: Acts as a mediator between Model and View, handling user interactions and updating the UI.
Benefits: Decoupling UI and logic simplifies testing and enhances code maintainability.
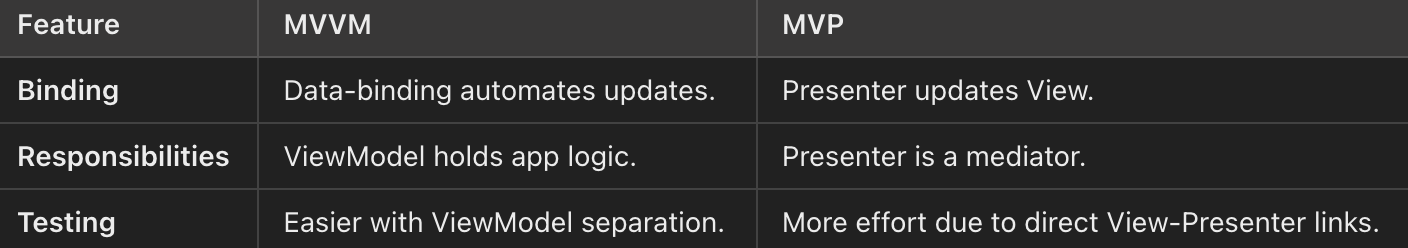
41. How is MVVM different from MVP?
- MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel): Utilizes two-way data binding, where the View automatically updates when the ViewModel data changes.
- MVP: Requires the Presenter to manually update the View.
42. How can you explain the Singleton design pattern?
The Singleton design pattern ensures that a class has only one instance and provides a global access point to it.
Use Cases: Shared resources like databases, configuration settings, or network managers.
43. How do you handle configuration changes in Android using ViewModel?
- Persistent Data: Store UI-related data in a
ViewModel. It survives configuration changes like screen rotations. - LiveData: Use LiveData in the ViewModel to observe and automatically update the UI.
44. What is the Repository pattern, and why is it useful?
The Repository pattern separates data access logic from business logic, acting as an intermediary between the data source and the rest of the application.
Benefits:
- Centralizes data access logic.
- Simplifies switching between data sources (e.g., API and local DB).
- Improves testability by mocking repository behavior.
45. How do you securely store sensitive information in Android?
- Keystore: Use for secure cryptographic key storage.
- EncryptedSharedPreferences: Encrypts data stored in preferences.
- Avoid Hardcoding: Never store sensitive information in code.
- Secure Communication: Use HTTPS and TLS for data transfer.
- Obfuscation: Minimize reverse engineering risks with ProGuard or R8.
46. How can you explain how to secure an Android app?
Steps to Secure an Android App:
- Use biometric authentication or multi-factor authentication.
- Employ encryption for local storage and network communications.
- Implement certificate pinning to guard against man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Regularly audit the app for vulnerabilities.
- Follow best practices for API security, including token-based authentication.
47. What are Network Security Configurations?
Network Security Configurations allow developers to define custom security rules for network traffic in an app.
Features:
- Restrict cleartext traffic.
- Enforce certificate pinning.
- Define domain-specific security settings.
Implementation: Use an XML file (network_security_config.xml) linked in the app’s manifest.
48. How can you prevent reverse engineering of an Android app?
- Obfuscation: Use tools like ProGuard or R8 to obfuscate the code.
- Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data and logic.
- Integrity Checks: Implement tamper detection.
- Proactive Tools: Use runtime protection mechanisms like DexGuard.
- Licensing: Employ license verification to deter unauthorized usage.
- Frequent Updates: Patch vulnerabilities regularly to stay ahead of threats.
49. What are coroutines?
Coroutines in Android are a powerful concurrency framework provided by Kotlin to simplify asynchronous programming. They help manage tasks that might block the main thread, such as network requests, database operations, or complex computations, while keeping your code readable and concise.
Key Features of Coroutines:
- Lightweight: Coroutines are more memory-efficient than traditional threads. You can run thousands of coroutines without significant memory overhead.
- Structured Concurrency: They are tied to a lifecycle (like
ViewModelorActivity), ensuring that tasks are automatically canceled when the lifecycle ends. - Suspend Functions: Functions marked with
suspendallow you to write asynchronous code sequentially. You can use them with keywords likeawaitorwithContextto handle background tasks. - Built-in Lifecycle Awareness: Using
LifecycleScopeorViewModelScope, you can ensure coroutines are canceled automatically when their associated lifecycle ends, reducing memory leaks. - Error Handling: Coroutines provide structured error handling using
try-catchorCoroutineExceptionHandler.
50. What are Flows?
Flows are part of Kotlin's coroutines library, designed to handle asynchronous data streams in a more structured and efficient way. They are especially useful for emitting multiple values sequentially over time, making them a perfect fit for scenarios like observing data changes in real-time.
Key Characteristics of Flows:
Cold Stream:
A flow is "cold" by default, meaning it does not emit data until it is actively collected. This helps in saving resources as it only processes when needed.
Asynchronous:
Flows run within coroutines and can be used to handle data asynchronously, avoiding UI thread blocking.
Lifecycle-Aware Integration:
Flows work seamlessly with Android's
LifecycleOwnerto ensure that data is collected only when the associated lifecycle is active, reducing the risk of memory leaks.
Basic Components of Flows:
Flow: Represents a cold stream of values that can be emitted sequentially.SharedFlow: Represents a hot stream of values shared across multiple collectors. Useful for events.StateFlow: A hot flow that holds and emits the latest value. Ideal for UI state management.